An operator specifies an operation to be performed that yields a value.
1.Arithmetic operators
2. Assignment operators .
3. Increment and Decrement operators
4. Relational operators.
5. Logical operators
6. Conditional operator
7. Comma operator
8. Sizeof operator
9. Bitwise operators
10. Other operators
1. Arithmetic operators: It is used for numeric calculations.
They are of two types:
1. Unary Arithmetic Operators
2. Binary Arithmetic Operators
Unary Arithmetic Operators: Unary operators require only one operand. For e.g +x -y
Binary Arithmetic Operators: Binary operators require two operands. There are five binary arithmetic operators.
Integer Arithmetic: In which both operands are integer
Floating-Point Arithmetic: In which both operands are integer type.
2. Assignment Operator : A value can be stored in a variable with the use of assignment operator.
The operator ‘=’ is used in assignment operator & statement.
3. Increment/ Decrement Operators: These are the unary operators because they operate on a single operand. Increment(++) and decrement(--) used to increase and decrease the value by 1.
2. Postfix Increment/ Decrement:
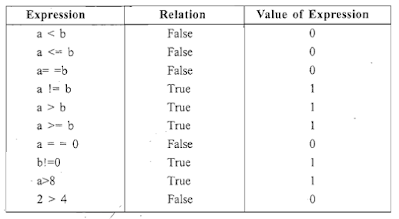
4. Relational Operators:
It is used to compare values of two expressions depending on their relationship.
Let us take two variables a=9 and b=5 . Evaluate the value.
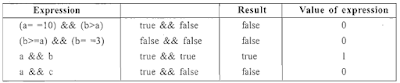
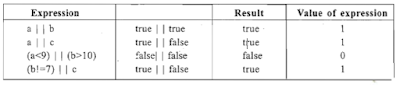
5. Logical Operators: An expression that combines two or more expressions in terms of logical expression. The operator returns 0 for false and 1 for true.
1.AND(&&) Operator: This gives true if both conditions are true, otherwise the result is false.
2. OR(||) Operators: This operator gives results false , if both conditions are false, otherwise the result is true.
3. Not(!) Operator: This is a unary operator and it negates the value of the condition . If the value of the condition is false then it gives the value true.
6. Conditional Operator: Conditional operator is a ternary (? And :) which requires three expressions as operands.
Syntax: TestExpression ? Expression1: Expression2
e.g. a > b ? a : b
Suppose a=5 and b=8 then,
Max=a > b ? a : b
Sizeof Operator: It is a unary operator . This operator gives the size of its operand in terms of bytes . The operand can be variable, constant or any data types( int, float, char etc)





















No comments:
Post a Comment